Imagine being able to track and visualize every part of your LangChain script in detail. That's what LangChain Debugger does, working smoothly with AimOS.
We'll look at a sample script to see how well LangChain Debugger and the scripts work together. It will highlight the main features of LangChain Debugger which logs LLMs prompts and generations, tools inputs/outputs, and chains metadata.
In this guide, we will prompt "What are the number of parameters in OpenAI’s GPT5 (based on rumors) and GPT4? What is the logarithm (base e) of the difference between the number of parameters?
AimOS 🔍 — A user-friendly observability platform for AI systems. It's adaptable, scalable, and versatile.
Executing LangChain Debugger: A Step-by-Step Guide
Let's do a practical example using a script to interact with LangChain to show how well it works with AimOS and LangChain Debugger.
Setting Stage
Before diving into the script, ensure that LangChain Debugger is installed and properly configured. If not, head over to the AimOS GitHub page for installation instructions: https://github.com/aimhubio/aimos.
Sample Script
1. Importing Required Modules
We begin by importing the necessary modules for LangChain and AimOS interaction.
from aimstack.langchain_debugger.callback_handlers import GenericCallbackHandler
from langchain.agents import AgentType, initialize_agent, load_tools
from langchain.llms import OpenAI2. Configuring Callbacks and LangChain LLM
Establish a callback mechanism using LangChain Debugger's GenericCallbackHandler and set up the LangChain LLM (Large Language Model) using OpenAI.
aim_callback = GenericCallbackHandler(repo_path="aim://0.0.0.0:53800")
callbacks = [aim_callback]
llm = OpenAI(temperature=0, callbacks=callbacks)Ensure that your AimOS server is active on the default 53800 port. In this instance, the server is running on the local machine. You can start an AimOS server effortlessly with the following command:
aimos server3. Loading Tools and Initializing Agent
Load the required tools for your LangChain script, initialize the agent, and set the agent type as ZERO_SHOT_REACT_DESCRIPTION.
tools = load_tools(["serpapi", "llm-math"], llm=llm, callbacks=callbacks)
agent = initialize_agent(
tools,
llm,
agent=AgentType.ZERO_SHOT_REACT_DESCRIPTION,
callbacks=callbacks,
)4. Running LangChain Script
Execute your LangChain script within the agent using the run method.
agent.run(
"What are the number of parameters in GPT5 and GPT4? What is the logarithm (base e) of the difference between the number of parameters?"
)5. Flushing Callbacks
Ensure that callbacks are flushed after running the script to capture the trace.
aim_callback.flush()After completing these steps, you will successfully log all actions on AimOS. Now, let's run the AimOS UI to observe the tracked metadata. To do this, navigate to the folder where the .aim repository is initialized and simply execute:
aimos ui😊 Enjoy this preview of what you'll see once you visit the provided URL:
Interpreting the results
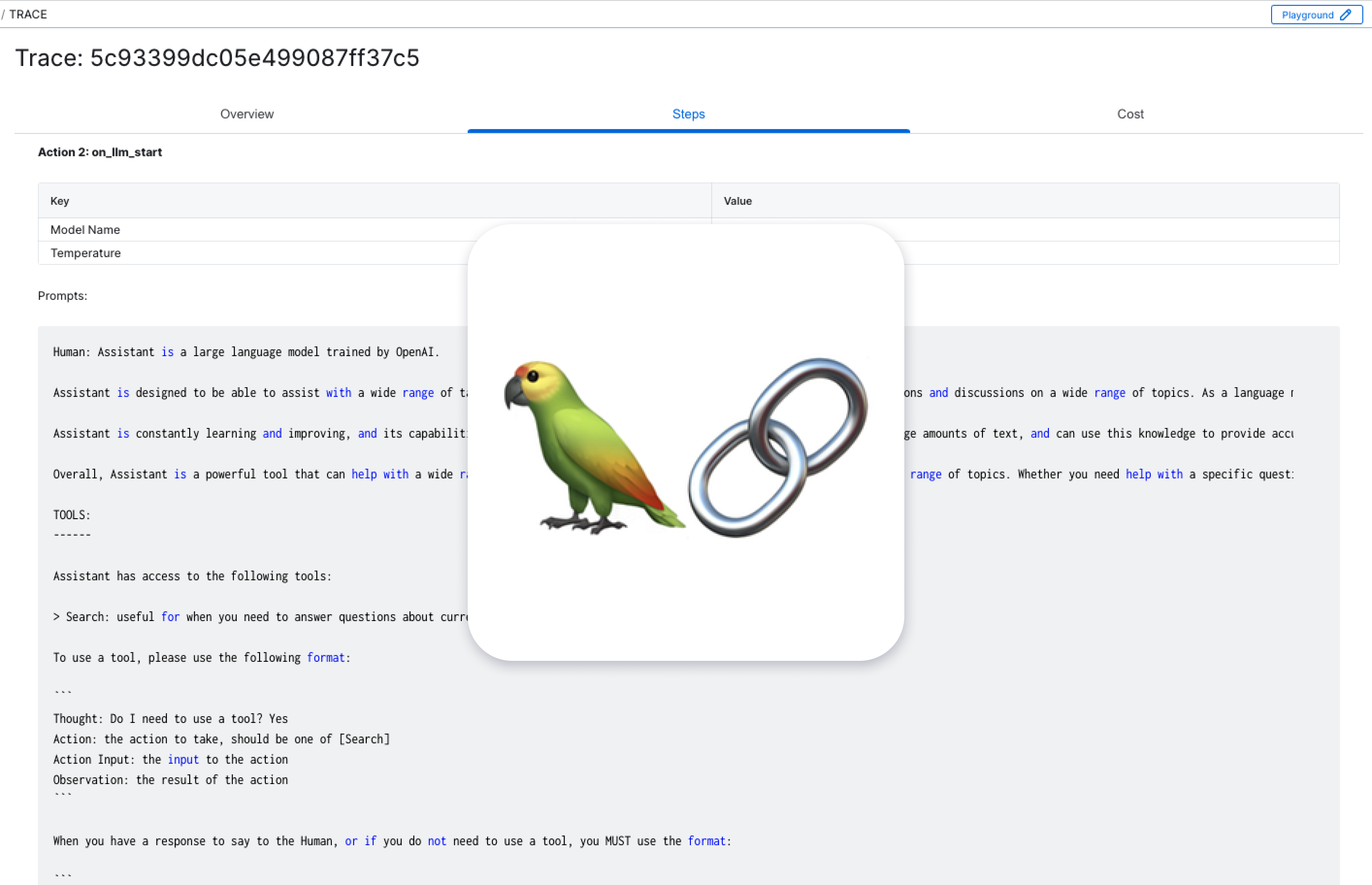
Head over to the AimOS Traces page to witness the detailed trace of your LangChain script. This page provides a comprehensive overview of every action and interaction within your LangChain environment.
Here you'll find a new trace corresponding to each query in the script. You can get valuable information by checking the Overview, Steps, and Cost tabs. These will show the details about the script’s execution, token use, and the costs involved.

Overview: Key Elements
Navigate through the Overview tab to grasp essential information:
Trace: A unique identifier for each trace, allowing you to easily reference and analyze specific interactions.
Total Steps: The number of actions or queries performed in a trace, providing a quick measure of complexity
Total Tokens: The total number of tokens is represented to understand the computational load of your queries, ensuring optimal performance.
Cost: This represents the total cost of the trace which is a critical factor in resource management, the cost breakdown helps you make informed decisions.

Steps: Exploring the Process
The Steps tab provides a detailed walkthrough of the sequence of actions undertaken throughout the pipeline to achieve the specified goal. In our example, the Agent executed a total of 18 steps to successfully accomplish the task.
Here's a breakdown of the pivotal actions:
- LLM Response: The Language Model (LLM) initially determines that, for the given question, it needs to utilize the Search tool to identify the person in question.
- Search Tool Execution: The LLM activates the Search tool to acquire the necessary information, successfully obtaining the desired output.
- LLM Decision: Subsequently, the LLM decides to employ the Search tool once again to retrieve additional details, such as the the number of parameters in GPT5 (based on rumors) and GPT4.
- Search Tool Execution: The Agent, following the LLM's decision, triggers the Search tool once more, fetching the required information.
- Calculator Tool Usage: With the obtained number, the Agent employs the Calculator tool to calculate the logarithm (base e) of the difference between the number of parameters.
- Final Answer: Lastly, armed with all the necessary information, the LLM crafts the complete answer to the original question and returns it.


Cost: Evaluating Resource Usage
In the Cost tab, you can examine three graphs showing token-usage, token-usage-input, and token-usage-output, providing a detailed breakdown of the computational costs associated with your LangChain activities.
- On the x-axis, you can see the steps, which represent the number of times the system made an API request to an LLM (Language Model).
- On the y-axis, you can see the number of tokens sent or received.

Wrapping up
The LangChain Debugger in AimOS is a powerful tool for deepening your understanding and gaining in-depth insights into your LangChain script. It logs LLMs prompts and generations, tools inputs/outputs, and chains metadata. It's great for both experienced users and beginners, offering a comprehensive observability.
For further insights into AI system monitoring and observability of software lifecycle, check out our latest article on the AimStack blog.
Learn more
AimOS is on a mission to democratize AI Systems logging tools. 🙌
Try out AimOS, join the Aim community, and contribute by sharing your thoughts, suggesting new features, or reporting bugs.
Don’t forget to leave us a star on GitHub if you think AimOS is useful, and here is the repository of Aim, an easy-to-use & supercharged open-source experiment tracker.⭐️